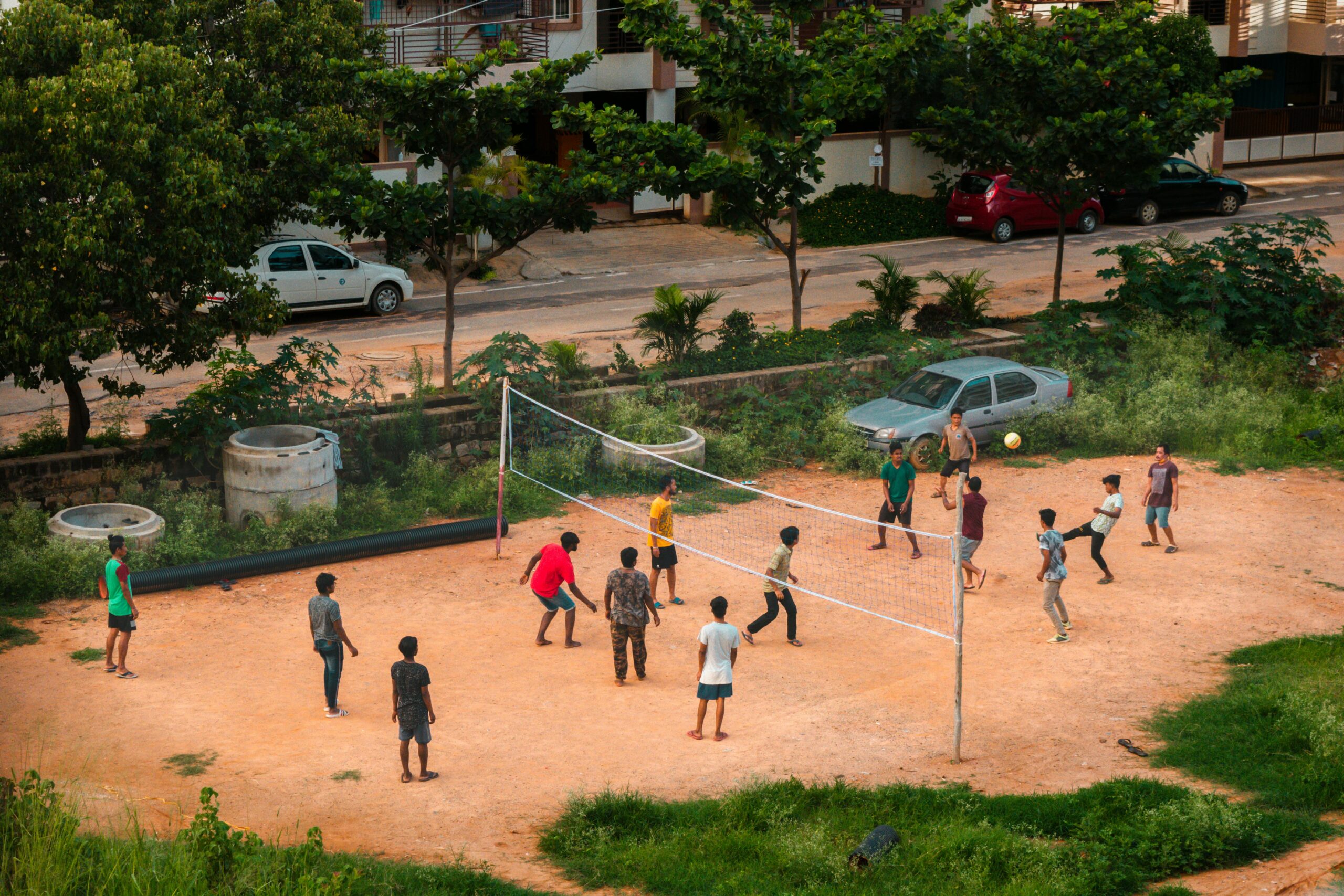
Raising a barely legal delinquent teen can be one of the most challenging experiences for any parent or guardian. But how do you keep a rebellious teen busy with engaging activities that actually work? If you’ve been struggling to find effective ways to channel their energy and reduce troublemaking, you’re not alone. This article dives deep into proven strategies to keep delinquent teens busy, offering fresh ideas that go beyond the usual advice. Wondering what activities can truly captivate a restless teen on the edge of adulthood? We’ve got you covered.
Many parents ask, “What are the best productive hobbies for rebellious teens?” or “How to stop a barely legal delinquent from falling into destructive habits?” The truth is, simply telling a teen to “stay busy” isn’t enough—and it definitely won’t keep them off the streets or away from bad influences. Instead, you need creative, hands-on solutions that spark their interest and build essential life skills. From adrenaline-pumping sports to tech-savvy projects, this guide reveals how to turn your teen’s energy into something positive and meaningful. Curious about how to keep your teen engaged without nagging or constant supervision? The answer lies in tailored delinquent teen activities that promote growth and responsibility.
In this post, we’ll explore effective ways to manage barely legal delinquent teens by filling their time with activities that reduce risky behavior and inspire self-improvement. Whether you’re looking for after-school programs for at-risk youth, outdoor adventures for troubled teens, or creative outlets that encourage expression, you’ll find actionable tips right here. Don’t let frustration take over—discover how to transform your teen’s downtime into a powerful tool for change. Ready to unlock the secrets to keeping your delinquent teen busy and focused? Let’s dive in!
7 Proven Strategies to Keep Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Engaged and Productive
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens can be a real challenge, especially in places like New York where the pace of life is fast and the distractions are many. Keeping these young adults engaged and productive is essential, not just for their personal development but also for reducing legal troubles and improving community safety. But how to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy with engaging activities? It’s not an easy question to answer, and sometimes the usual advice just doesn’t cut it. Here, we explore 7 proven strategies that can help parents, guardians, or legal professionals to guide these teens toward a better path.
Understanding Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Before jumping into strategies, it’s important to know what “barely legal delinquent teens” means. These are youth who have just reached the age of majority—usually 18 years old—but still show patterns of delinquent behavior such as minor offenses, truancy, or substance abuse. They often fall through the cracks of juvenile systems and adult legal frameworks, making intervention more complicated. Knowing this, strategies should be tailored to their unique needs, balancing accountability with support.
1. Vocational Training and Job Opportunities
One of the most effective ways to keep barely legal delinquent teens engaged is by offering them vocational training or real job opportunities. These teens often lack direction or marketable skills, leading to frustration and bad choices. Vocational programs provide practical skills in fields such as:
- Carpentry
- Automotive repair
- Culinary arts
- Information technology
In New York, many community centers and non-profits offer free or low-cost training. Getting a part-time job also helps teens to develop responsibility, time management, and a sense of accomplishment. Even if it’s not a permanent employment, the experience matters.
2. Structured Recreational Activities
Physical activity plays a big role in channeling youthful energy positively. Sports leagues, fitness classes, or outdoor adventure clubs can do wonders. These activities helps to reduce stress, build teamwork skills, and keep teens away from trouble. Some examples include:
- Basketball or soccer teams
- Martial arts classes
- Hiking or camping groups
New York offers many public parks and recreation programs accessible to teens from different backgrounds. Structured recreational time also creates a routine, which is often missing in delinquent teens’ lives.
3. Mentorship Programs
Having a mentor can change a teen’s life, but finding the right one is crucial. Mentors provide guidance, emotional support, and a positive adult role model. Mentorship programs are especially effective for those who lack stable family support. Mentors can be:
- Community leaders
- Volunteers from local organizations
- Professionals in fields the teen is interested in
Research shows that teens with mentors are less likely to engage in criminal activities and more likely to succeed academically and socially.
4. Creative Arts Engagement
Many barely legal delinquent teens express themselves better through art than words. Music, painting, writing, and theater can provide a non-judgmental outlet for emotions and frustrations. New York has a vibrant arts scene and many community programs offering workshops or classes. Creative arts help teens to:
- Develop self-esteem
- Explore identity
- Connect with others
For example, joining a local theater group or a music production class might spark new interests and talents.
5. Legal Education and Awareness
Sometimes, delinquent behavior comes from ignorance about consequences and legal rights. Providing teens with knowledge about the legal system, their rights, and responsibilities can empower them to make better decisions. Workshops or seminars led by legal professionals or organizations can demystify the justice system. This strategy also helps teens understand the long-term impact of their actions on their future.
6. Community Service and Volunteer Work
Involving teens in community service can build empathy and a sense of belonging. Volunteer work also adds structure to their time and helps them develop skills like teamwork and communication. Some ideas for community service include:
- Environmental clean-up projects
- Helping at food banks
- Assisting elderly neighbors
Programs in New York often connect youth with local nonprofits needing help. Community service also looks good on resumes and college applications, motivating teens to participate.
7. Counseling and Mental Health Support
Many barely legal delinquent teens struggle with underlying mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, or trauma. Providing access to counseling services is critical. Mental health support can come in various forms:
- Individual therapy
- Group counseling sessions
- Substance abuse programs
New York has numerous resources, including public health clinics and school-based counselors. Addressing mental health not only reduces delinquent behavior but also improves overall well-being.
Summary Table of Strategies
| Strategy | Benefits | Examples in New York |
|---|---|---|
| Vocational Training | Skill building, employment | Community colleges, trade schools |
| Structured Recreation | Physical health, routine |
How to Channel the Energy of Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Into Positive Activities
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens can be one of the most challenging experiences, especially for parents, guardians, and legal professionals in New York. These youths, often caught between childhood and adulthood, may struggle with authority, social norms, and personal direction. But instead of letting this energy go wasted in unproductive or harmful behaviors, it’s possible to channel it into positive activities that build character, skills, and self-respect. This article explores how to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy with engaging activities, providing practical tips, historical context, and examples that can make a real difference.
Understanding Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Barely legal teens, typically ages 17 to 19, are in a tricky phase of life. They legally become adults in many respects but might still lack the maturity or guidance needed to make good decisions. Historically, this age group has been linked with higher rates of risk-taking and delinquent acts. In New York, the juvenile justice system often faces difficulties because these teens fall into a gray area between juvenile and adult court, making intervention and rehabilitation more complex.
Engagement is key for these young people because idle time often leads to trouble. The National Institute of Justice reports that structured activities reduces recidivism among youths by providing a sense of purpose and belonging. So how do you keep them busy with something that actually helps?
How to Channel Their Energy Into Positive Activities
Redirecting the energy of barely legal delinquent teens doesn’t mean forcing them into activities they hate. It is more about finding what interests them and building on it. Here are some practical ideas:
Sports and Physical Activities
- Join a local basketball or soccer league.
- Try martial arts or boxing classes that teach discipline.
- Volunteer for community clean-ups or park restoration projects.
Creative Arts
- Enroll in music or art classes, like guitar lessons or painting.
- Participate in theater groups or spoken word poetry.
- Use social media platforms to share their creative work positively.
Vocational Training
- Learn a trade such as carpentry, plumbing, or automotive repair.
- Attend workshops offered by local community colleges.
- Intern with local businesses in fields they interested in.
Community Service and Mentoring
- Volunteer at shelters, food banks, or animal rescue centers.
- Become mentors for younger kids in after-school programs.
- Join youth advisory boards or local government youth councils.
Why Engagement Helps Prevent Recidivism
Engagement in meaningful activities provides structure that delinquent teens often lack. When they busy themselves with positive pursuits, their chances of returning to criminal behaviors decrease significantly. The U.S. Department of Justice explains that adolescents who have access to constructive activities develop better decision-making skills and self-esteem.
Also, positive involvement strengthens social bonds with peers and adults, which acts as a protective factor against delinquency. Teens who feel connected to their community and see a future for themselves are less likely to engage in negative behaviors.
How to Keep a Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy: Practical Tips
Keeping a barely legal delinquent teen busy isn’t always easy, especially when motivation is low or past experiences have been negative. Here are some tips that might help:
- Listen to Their Interests: Don’t impose activities that seem boring or irrelevant. Instead, ask what they like or want to try.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break down larger aspirations into smaller, achievable steps.
- Create a Routine: Stability can be very helpful. A daily schedule with time for work, study, and leisure can reduce temptation.
- Reward Progress: Celebrate achievements, no matter how small, to build confidence.
- Involve Them in Decision-Making: Giving teens some control fosters responsibility and ownership.
- Connect with Professionals: Counselors, social workers, and legal advocates can provide resources and support.
Comparing Different Activity Types for Delinquent Teens
| Activity Type | Benefits | Potential Challenges | Example in NYC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sports | Builds teamwork, discipline | Risk of injury, cost of equipment | YMCA basketball leagues |
| Creative Arts | Enhances expression, self-esteem | May need supplies or space | Local art centers like the Bronx Art Space |
| Vocational Training | Job skills, sense of purpose | Requires commitment | Bronx Community College workshops |
| Community Service | Builds empathy, social bonds | Time-consuming, emotional strain | Food banks like City Harvest |
Addressing the Term “Dickdrainers” in Context
The phrase “dickdrainers” appears non-standard and possibly derogatory slang that might be used in some circles to describe delinquent teens or troublemakers. It’s important to approach such terms with sensitivity, especially when dealing with legal
Top 10 Engaging Activities to Prevent Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Boredom
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens can be really challenging, especially when boredom starts creeping in. In New York, where legal issues and juvenile delinquency intersect often, keeping these teens engaged is not just about passing time but about steering them away from trouble. Parents, guardians, and even legal professionals sometimes wonder how to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy with engaging activities because, honestly, when boredom strikes, trouble might follow. This article digs into top 10 engaging activities to prevent barely legal delinquent teen boredom and offers practical tips that might just make a difference.
Why Boredom Is Risky for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
First, it’s important to understand why boredom is such a big deal for teens who are barely legal and have a delinquent streak. Studies, including those from juvenile justice programs in New York, show that boredom often leads these teens to seek thrills or peer approval through risky behaviors — like vandalism, petty theft, or drug use. When their time is idle, they feel disconnected, misunderstood, or unchallenged, which may push them toward negative choices. So, keeping them busy is not just a casual suggestion but a strategic move to reduce recidivism or repeat offenses.
Top 10 Engaging Activities to Prevent Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Boredom
Below is a mixed list of activities that can be done with limited resources and may help channel energy positively. The idea isn’t perfection but engagement through diverse options.
Community Service Projects
Getting teens involved in local community clean-ups, food banks, or charity events helps them see purpose beyond themselves. It also builds a sense of responsibility and belonging.Creative Arts and Expression
Drawing, painting, or writing poetry can help teens express feelings they might not verbalize. Art therapy has been used in juvenile programs as a constructive outlet.Sports and Physical Activities
Organized sports like basketball or soccer leagues, or even simple jogging groups around the neighborhood, give an outlet for physical energy and build teamwork skills.Vocational Training Workshops
Learning skills like carpentry, cooking, or computer basics opens doors for future employment and instills pride in accomplishment.Mentoring Programs
Pairing teens with positive role models or mentors from legal aid organizations or youth groups creates support networks and guidance.Music Lessons or Band Participation
Playing an instrument or joining a local band can be both fun and challenging, providing structure and a sense of achievement.Outdoor Adventure Activities
Hiking, camping, or even simple nature walks connect teens with the outdoors, reduce stress, and encourage teamwork.Educational Tutoring and Homework Clubs
Academic support can boost confidence and reduce school-related frustrations that sometimes lead to delinquency.Entrepreneurship or Business Clubs
Encouraging teens to start small projects like lawn mowing services or crafts sales promotes responsibility and financial literacy.Legal Awareness Workshops
Understanding the consequences of certain behaviors through workshops led by attorneys or legal experts can empower teens to make informed choices.
How To Keep A Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy — Practical Tips
Keeping teens engaged takes effort and creativity. Here’s a simple outline of actions that caregivers and professionals can take:
- Set Clear Expectations and Boundaries: Teens respond better when they knows limits and consequences, but also when they understand the reasons behind rules.
- Offer Choice and Autonomy: Giving teens options within structured activities lets them feel control, which lessens resistance.
- Encourage Small Goals: Breaking down bigger goals into manageable steps motivates continued participation.
- Be Consistent but Flexible: Routine helps, but being adaptable to mood swings or interest shifts keeps teens from feeling trapped.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Rewards and recognition for participation or progress encourage sustained engagement.
- Connect Activities to Personal Interests: Whether it’s music, sports, or tech, tailoring activities makes teens more likely to stick around.
- Involve Peer Groups: Sometimes teens listen more to peers than adults, so group activities can foster positive peer pressure.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regular check-ins help identify what’s working and what’s not, allowing for timely adjustments.
Comparison of Activities Based on Engagement and Skill Development
| Activity Type | Engagement Level | Skill Development | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Community Service | High | Moderate | High |
| Creative Arts | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Sports | High | Moderate | High |
| Vocational Training | Moderate | High | Variable |
| Mentoring | Moderate | Variable | Moderate |
| Music Lessons | Moderate | High | Variable |
| Outdoor Adventures | High | Low | Moderate |
| Educational Tutoring | Moderate | High | High |
| Entrepreneurship | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Legal Workshops | Low |
Expert Tips: Keeping Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Busy Without Conflict
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens is never an easy journey, especially in a busy city like New York where distractions and challenges seem endless. Parents, guardians, or even legal professionals often find themselves asking, “How to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy without conflict?” This is not just a question of keeping teens occupied, but also about steering them toward positive engagements that reduce risks and potential legal troubles. In this article, we dive into expert tips, practical activities, and real-world strategies that can help manage and engage these young adults in a constructive way.
Why Keeping Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Busy Matters
Barely legal teens, usually around 17 to 19 years old, are at a critical transition point. They face pressures from peer groups, legal responsibilities, and their own search for identity. When left idle, especially those with delinquent tendencies, they may fall into trouble more easily. Studies have shown that engagement in structured activities lowers chances of recidivism and improves social skills, self-esteem, and future prospects.
A quick historical note: The juvenile justice system in New York has evolved to focus more on rehabilitation rather than punishment, especially for teens nearing adulthood. This means that keeping teens busy with positive outlets is now more supported by community programs and legal frameworks.
How To Keep A Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy With Engaging Activities
It’s not just about filling time. The key is finding activities that resonate with the teen’s interests, challenge them, and help develop skills that can later assist with employment or education. Here are some expert-approved ways:
- Community Service and Volunteer Work: Many delinquent teens find purpose when helping others. It could be cleaning parks, assisting in food banks, or participating in charity events. These activities build empathy and responsibility.
- Vocational Training Programs: New York offers various vocational schools or community centers where teens can learn trades like carpentry, plumbing, or culinary arts. These provide practical skills and sometimes certifications.
- Sports and Physical Activities: Joining local sports leagues or martial arts classes helps with discipline and provides a healthy outlet for energy. It also encourages teamwork.
- Creative Arts: Engaging in music, painting, theater, or dance can be therapeutic. Many teens express themselves better through art, which can prevent conflict.
- Job Shadowing or Internships: For those close to legal adulthood, internships in local businesses or shadowing professionals might give them a glimpse of future career paths.
Conflict-Reducing Strategies When Engaging Delinquent Teens
It’s no secret that conflict can arise when trying to guide a delinquent teen. Often, it’s because they feel misunderstood or controlled. Here are some strategies to keep the peace:
- Offer Choices Instead of Commands: Giving them options, like choosing between two activities, helps teens feel they have control.
- Set Clear but Flexible Rules: Boundaries are necessary, but teens resist when rules seem arbitrary. Explain reasons behind rules to encourage cooperation.
- Listen Actively: Sometimes teens just want someone to hear their side without judgment. This reduces defensiveness.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Praise small achievements to motivate continuous effort.
- Avoid Power Struggles: When conflict escalates, stepping back and revisiting the issue later can be more effective.
Practical Examples for Keeping Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Busy
Imagine a 17-year-old named Jake who frequently skips school and gets into minor trouble. His legal guardian enrolls him in a community woodworking class, where Jake learns to make furniture. He feels proud seeing his finished projects and even starts selling small items online, which improves his self-esteem. Meanwhile, Jake volunteers at a neighborhood food pantry once a week, connecting with other youth and adults positively. His guardian notices fewer arguments at home because Jake feels respected and busy.
Another example is Maria, who struggles with anger and has had several run-ins with the law. Her counselor suggests joining a local boxing gym to channel her aggression healthily. Alongside, she starts attending art therapy sessions that help her express feelings she struggles to verbalize. This combination reduces her outbursts and keeps her away from negative influences.
Common Misconceptions and Comparisons
Some people think that barely legal teens with delinquent behavior only need strict discipline or legal penalties to improve. However, research and expert opinions show that positive engagement and understanding yield better long-term results than punishment alone.
Comparing two approaches:
| Approach | Outcome | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Strict Punishment | May cause resentment, rebellion | Short-term compliance, long-term issues |
| Structured Positive Engagement | Builds skills, reduces recidivism | Encourages growth and responsibility |
Another myth is that teens will naturally “grow out” of delinquent behavior without intervention. While some do, many require guidance and opportunities to change paths, especially when close
What Are the Best Hobbies for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens to Stay Out of Trouble?
What Are the Best Hobbies for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens to Stay Out of Trouble?
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens can be really challenging for parents, guardians, and even legal professionals in New York. These young adults—often between 17 to 19 years old—stand at the crossroads of childhood and adulthood. Their behaviors sometimes lean to the edge of trouble, making it super important to find ways to keep them occupied with positive activities. But what hobbies really works best? And how do you keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy with engaging activities that actually reduce the chances of them falling into trouble? This article explores practical ideas and legal insights focused on helping these teens find a better path.
Why Hobbies Matter for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Hobbies aren’t just time-fillers, they serve as crucial outlets for energy and emotions. For teens who had brushes with the law or risky behaviors, having a constructive routine can reduce impulsiveness and keep them away from negative peer influences. Historically, youth programs and recreational activities have proven to lower recidivism rates—meaning teens who engage in sports, arts, or vocational training are less likely to reoffend compared to those who lack structured pastimes.
In New York, juvenile justice initiatives often encourage community-based programs that focus on skill-building and mentorship. These support systems show how important it is to channel teen energy productively.
How To Keep A Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy With Engaging Activities
It’s easier said than done, right? Keeping a teen busy who might be resisting authority or bored with conventional activities is tricky. Here is a list of creative and effective hobbies that can appeal to different interests and personality types:
1. Sports and Physical Activities
- Basketball or soccer leagues
- Martial arts classes (karate, judo, boxing)
- Skateboarding or BMX biking
- Dance classes (hip-hop, breakdancing)
Physical activities are great for channeling aggression or restlessness. They also teach discipline and teamwork, which are valuable life skills.
2. Artistic and Creative Pursuits
- Graffiti art or street art workshops
- Music lessons (guitar, drums, DJing)
- Writing poetry or rap lyrics
- Theater or drama clubs
These hobbies allow teens to express themselves in non-destructive ways. Plus, creative outlets can boost self-esteem and reduce feelings of isolation.
3. Vocational and Skill-Based Programs
- Automotive repair workshops
- Culinary arts or baking classes
- Computer coding or graphic design courses
- Carpentry or welding programs
Learning a trade can provide teens with a sense of purpose and a potential career path, keeping them focused on future goals.
4. Volunteering and Community Service
- Animal shelters
- Local food banks
- Environmental cleanups
- Youth mentorship programs
Giving back helps teens build empathy and a connection to their community, which can be transformative for someone feeling disconnected.
Comparing Hobbies: What Works Best?
Some might think sports are the only answer, but not all teens are athletically inclined. Here is a simple comparison table to help parents and legal counselors decide what might be a good fit:
| Activity Type | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Sports | Physical fitness, discipline | Risk of injury, requires teams |
| Artistic Pursuits | Emotional expression, creativity | May need materials, less social |
| Vocational Training | Job skills, future focus | May seem boring, needs commitment |
| Volunteering | Builds empathy, community ties | Time-consuming, depends on availability |
Tips for Parents and Legal Professionals in New York
- Find programs that cater specifically to at-risk youth; many community centers offer free or low-cost options.
- Encourage teens to try multiple activities before sticking to one; sometimes they need to explore to find interest.
- Involve teens in decision-making to give them ownership over their hobbies, which increases commitment.
- Legal professionals can collaborate with social workers and community programs to create support networks for delinquent teens.
- Avoid pressuring teens too much; hobbies should feel like fun, not another chore.
Practical Examples From New York Programs
- The Bronx Youth Empowerment Program offers basketball and coding classes that have helped many teens avoid reoffending.
- Brooklyn Arts Council runs street art workshops that channel creative energy into public projects.
- Queens Vocational Training Center provides culinary courses aimed at teens who want to enter hospitality careers.
- Manhattan Volunteer Corps connects teens with local nonprofits for hands-on community work.
These examples show how diverse options exist and how they can be tailored to meet individual needs.
In the end, keeping a barely legal delinquent teen out of trouble needs more than just telling them to “stay busy.” It requires patience, understanding, and a willingness to explore varied hobbies that interest
Transforming Barely Legal Delinquent Teens: Creative Ways to Build Responsibility
Transforming Barely Legal Delinquent Teens: Creative Ways to Build Responsibility and Keep Them Busy
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens is never easy, especially in bustling places like New York where distractions and temptations are everywhere. Parents, guardians, and legal professionals often find themselves asking, how to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy with engaging activities that could also build their sense of responsibility? It’s a challenge that requires creativity, patience, and understanding. The wrong approach might push them away, while the right one can transform their lives dramatically over time.
Understanding Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
First thing first, what does “barely legal delinquent teen” even means? Typically, these are young people around 18 years old, who just crossed the threshold into legal adulthood but still struggle with minor crimes, rebellious behavior, or lack of direction. They might have brushes with law enforcement, but not necessarily serious felonies yet. It’s a critical time because the choices they make now can set the tone for their entire adult life.
Historical context shows that youth delinquency has always been part of societal challenges, but the modern environment with social media, peer pressure, and economic stress adds layers of complexity. In New York, where diversity and fast-paced living intersect, teens might feel overwhelmed or under pressure, leading to delinquent acts.
Why Building Responsibility Matters
Responsibility is more than just doing chores or following rules. For delinquent teens, it means learning to be accountable for their actions, understanding consequences, and developing self-discipline. When teens feel responsible, they are less likely to engage in risky or illegal behaviors. Responsibility also ties into self-esteem; when they succeed at something, they feel worth more.
Ways to build responsibility include:
- Assigning consistent, age-appropriate tasks at home or work
- Encouraging goal-setting and tracking progress
- Teaching financial literacy, like budgeting their own money
- Involving them in community service or volunteer work
- Offering leadership opportunities in clubs or sports
Creative Activities to Keep Teens Engaged
Keeping a barely legal delinquent teen busy is not about just filling their time, but providing activities that engage their mind and body, reducing chances to fall into negative habits or peer groups. Here are some creative ways:
Urban Gardening Projects: New York has many community gardens. Teens can learn about sustainability, responsibility, and patience by tending plants. It also connects them with positive community members.
Art and Music Workshops: Expressing emotions through art or music can be very therapeutic. Local programs often offer free or low-cost classes. It’s a healthy outlet for frustration or boredom.
Internships and Job Training: Partnering with local businesses or nonprofits to offer internships can teach work ethic and open career paths.
Sports and Physical Activities: Joining a team or even solo activities like running or martial arts help with discipline and physical health.
Legal Education Programs: For teens interested, learning about the law and their rights might inspire them to make better choices or even pursue legal careers.
Practical Examples of Responsibility Building
Imagine a teen named Jake, who was caught shoplifting and was on the verge of entering the adult criminal system. Instead of only punitive measures, his probation officer suggested he volunteer at a local food bank twice a week, while attending a job skills workshop. Over months, Jake started seeing himself differently — as someone who can contribute positively. He also joined a weekend basketball league and started saving money from a part-time job. These changes didn’t happen overnight, but with consistent support and activities, Jake’s life trajectory shifted.
Comparing Approaches: Punishment vs. Engagement
| Aspect | Punishment Approach | Engagement Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Consequences and deterrence | Skill-building and positive reinforcement |
| Teen’s Emotional Response | Often resentment or defiance | Increased self-worth and motivation |
| Long-term Effect | Risk of recidivism or alienation | Higher chances of rehabilitation |
| Community Impact | Minimal or negative | Positive, fosters social bonds |
The table shows that while punishment might seem straightforward, engagement through creative activities is more effective for long-term change.
How To Keep A Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy Dickdrainers?
Addressing the phrase “how to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy dickdrainers” is confusing and seems misplaced in a serious discussion. If it refers to keeping teens away from negative influences or harmful peer groups, the answer lies in structured support and engagement. Teens influenced by peers encouraging poor behavior need positive alternatives and role models.
Strategies include:
- Monitoring social circles and encouraging friendships with responsible peers
- Enrolling teens in groups or clubs with clear rules and goals
- Offering mentorship programs where older youth guide younger ones
- Providing safe spaces where teens can
How to Use Sports and Arts to Keep Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Motivated
Keeping teenagers, especially those who are barely legal and edging towards delinquency, busy and motivated is a challenge that many parents, educators, and legal professionals in New York face. These young adults often find themselves in a tricky space, where the law starts to treat them as adults, but their maturity and decision-making skills are still developing. Using sports and arts as tools can be powerful ways to channel their energy positively, preventing them from falling deeper into trouble. But how exactly can this be done effectively?
Why Focus on Sports and Arts for Delinquent Teens?
Sports and arts have long been recognized for their role in youth development. Historically, community programs in places like New York City have used basketball leagues, music classes, and theater workshops to keep at-risk youth engaged. These activities provide structure, discipline, and a sense of accomplishment. For barely legal teens, who are on the brink between adolescence and adulthood, such engagement can be the difference between staying on the right path or getting involved with the criminal justice system.
The law sometimes overlooks how much influence positive recreational activities have on behavior. When teens are kept busy with meaningful pursuits, they have less time to engage in delinquent acts. Moreover, these activities help them develop skills that are valuable for future employment or education.
How to Use Sports to Keep Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Motivated
Sports offer physical activity, social interaction, and a goal-oriented environment. Here’s how sports can be useful:
- Provides Routine: Scheduled practices and games give teens a regular timetable.
- Builds Teamwork: They learn to cooperate with others, which is critical for social development.
- Improves Self-esteem: Achieving sports goals boosts confidence.
- Teaches Discipline: Training requires commitment and self-control.
- Offers Positive Role Models: Coaches often serve as mentors and influence behavioral change.
In New York, programs like the Police Athletic League (PAL) have been successful in engaging at-risk youth through sports such as basketball, soccer, and boxing. These programs not only teach sports skills but also emphasize character development and community involvement.
Engaging Arts Programs for Barely Legal Teens
Artistic activities can be just as effective, offering a creative outlet for emotions and self-expression that might otherwise manifest in destructive ways.
- Encourages Emotional Expression: Painting, music, dance, and theater give teens a way to express feelings.
- Enhances Cognitive Skills: Learning an instrument or acting improves concentration and problem-solving.
- Fosters Cultural Connection: Arts connect teens to their heritage and community.
- Builds Patience and Persistence: Mastering an art skill is a long-term process.
- Promotes Positive Social Interaction: Group projects and performances create bonds among peers.
In New York City, various community centers and nonprofits offer free or low-cost arts programs targeting teens at risk for legal issues. These programs often collaborate with legal advocates to support youth who might be involved in the juvenile justice system.
Practical Ways to Keep Teens Busy With Engaging Activities
It is not enough to just introduce sports or arts; the key is maintaining consistent engagement. Below is a simple outline on how to keep barely legal delinquent teens busy:
- Identify Interests – Talk to the teen about what activities they enjoy or want to try.
- Connect to Local Programs – Find community centers, schools, or nonprofits that offer relevant sports or arts programs.
- Set Realistic Goals – Help them set short-term and long-term goals related to their activities.
- Provide Support – Encourage attendance, provide transportation if needed, and offer praise for progress.
- Monitor Progress – Stay involved and check how the activities affect their behavior and motivation.
- Encourage Peer Groups – Positive peer influence is crucial and can be reinforced through team or group participation.
- Involve Legal or Social Services – When necessary, coordinate with professionals to ensure the teen’s engagement aligns with any court or rehabilitation requirements.
Comparison Table: Sports vs Arts for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
| Aspect | Sports | Arts |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Activity | High – builds fitness and coordination | Low to moderate – depends on the art form |
| Emotional Expression | Limited but present through competition | High – direct outlet for feelings and creativity |
| Social Interaction | Team-based, competitive | Group projects, collaborative performances |
| Skill Development | Physical skills, strategy, teamwork | Cognitive skills, fine motor skills, emotional intelligence |
| Accessibility | Requires facilities and equipment | Often less equipment-heavy, more flexible |
| Long-term Benefits | Discipline, health, teamwork | Creativity, patience, problem-solving |
Why Keeping Barely Legal Teens Busy Matters Legally
From a legal perspective,
5 Life-Changing Volunteer Opportunities for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Navigating the challenge of keeping barely legal delinquent teens busy can feel like a never-ending battle for many parents, guardians, and even legal professionals in New York. These young individuals, often on the verge of adulthood but still grappling with impulsive behaviors or past mistakes, need positive outlets to channel their energies. Without the right guidance and opportunities, they might fall back into trouble or remain stuck in unproductive routines. So, what are some life-changing volunteer opportunities that can genuinely engage these teens and possibly steer them towards a better path? Let’s dive in.
Why Volunteer Opportunities Matter for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Volunteering does not just fill time; it transforms lives. For teens who have brushes with the law or are struggling to find a direction, giving back to the community can provide a sense of purpose and belonging. Historically, programs aimed at youth rehabilitation highlight that participation in community services reduces recidivism and builds social skills. When teens see firsthand how their actions impact others positively, it fosters empathy and responsibility.
In New York, many organizations tailor volunteer roles to fit the unique needs and capabilities of teens, especially those close to legal adulthood but still in a vulnerable phase. These opportunities help them develop soft skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving, which are crucial for future employment or education. Plus, volunteering can sometimes open doors for legal leniency or support from the courts.
5 Life-Changing Volunteer Opportunities for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Environmental Clean-Up Projects
Many cities and neighborhoods in New York offer community clean-up days. Teens can get involved in park restoration, river clean-ups, or urban gardening. This type of activity is hands-on and physically engaging, making it hard for bored teens to lose interest. Plus, it contributes to a cleaner environment, which benefits everyone.Animal Shelters and Rescue Centers
Working with animals has therapeutic benefits. For teens who’ve experienced trauma or instability, caring for animals can provide comfort and a non-judgmental space. Animal shelters often need help with feeding, cleaning, and socializing pets, which teaches responsibility and patience.Soup Kitchens and Food Banks
Feeding the hungry is a direct way to witness the impact of generosity. Barely legal teens volunteering at soup kitchens in New York City or upstate communities can learn humility and community values. It also offers a chance to meet diverse people and understand different life circumstances.Mentorship and Tutoring Programs
Some teens might find joy in helping younger kids with homework or life skills. Mentorship programs not only keep them occupied but also build leadership qualities. These roles require commitment and can improve the teen’s self-esteem as they see others benefit from their guidance.Arts and Culture Initiatives
For creative teens, volunteering at museums, theaters, or community art centers provides a platform to express themselves and engage with culture. These settings often need volunteers for organizing events, guiding visitors, or assisting in workshops, which can be both fun and educational.
How To Keep A Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy With Engaging Activities
Keeping a barely legal delinquent teen busy ain’t just about stuffing their schedule, but finding activities that hold their attention and challenge them in good ways. The goal is to replace negative habits with positive routines that feel rewarding. Here are some tips:
- Mix Physical and Mental Activities: Teens need to move and think. Sports, dance classes, or even martial arts can burn off excess energy. Meanwhile, puzzle clubs, coding workshops, or book groups stimulate the brain.
- Set Clear, Achievable Goals: Teens respond better when they know what they’re working towards. Whether it’s completing a volunteer project or mastering a skill, clear goals make activities purposeful.
- Encourage Social Connections: Having friends or peers involved can increase motivation. Group volunteering or team sports can build camaraderie and reduce feelings of isolation.
- Balance Freedom and Structure: Over-scheduling might backfire. Letting teens have some say in choosing activities gives them ownership and reduces resistance.
- Reward Progress: Small rewards for meeting milestones, like certificates or community recognition, can boost confidence and encourage continued engagement.
Practical Examples of Volunteer Schedules for Teens
Here’s a simple weekly outline that combines volunteer work with other productive activities:
| Day | Activity | Time Commitment | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monday | Soup kitchen volunteering | 3 hours | Empathy building, social skills |
| Wednesday | Animal shelter assistance | 2 hours | Responsibility, emotional support |
| Friday | Environmental clean-up | 3 hours | Physical activity, teamwork |
| Saturday | Mentorship/tutoring sessions | 2 hours | Leadership, academic skills |
| Sunday | Arts center volunteering |
The Ultimate Guide to Managing Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Behavior with Engaging Projects
The Ultimate Guide to Managing Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Behavior with Engaging Projects
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens can be one of the most challenging experiences for parents, guardians, or even legal professionals in New York. These youths, often caught between childhood and adulthood, sometimes get involved in behaviors that push legal boundaries. Keeping them busy with engaging activities is not just a recommendation but a necessity to steer them away from trouble. But how to keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy with engaging activities? This guide explores practical ways to manage these behaviors by introducing projects and activities that can channel their energy positively.
Understanding Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
Before jumping to solutions, it’s important to understand the nature of barely legal delinquent teens. “Barely legal” usually refers to those who are 18 or just reaching adulthood but still entangled in juvenile-like delinquent behavior. This group often faces legal consequences but also struggles with identity, peer pressure, and lack of direction.
Historically, juvenile delinquency has been linked to various social and economic factors, including family environment, education access, and community support. In New York, the juvenile justice system tries to balance between punishment and rehabilitation, recognizing that engagement in productive activities can reduce recidivism.
Why Engaging Projects Matter
Engagement means more than just keeping teens busy; it means giving them meaningful work that builds skills, confidence, and a sense of responsibility. When teens are involved in projects, they:
- Learn new skills that might open job opportunities
- Develop discipline and time management
- Build positive social relationships
- Reduce idle time, which often leads to trouble
Without engagement, barely legal delinquent teens risk falling deeper into negative behavior patterns or legal issues.
Types of Engaging Activities to Consider
There is no one-size-fits-all activity for every teen, but certain types of projects tend to work well for most. Here’s a list of engaging activities that could help keep a barely legal delinquent teen busy:
Community Service Projects
- Volunteering at local shelters or food banks
- Participating in neighborhood cleanups
- Helping with animal rescue operations
Vocational Training Programs
- Carpentry or construction basics
- Automotive repair workshops
- Culinary arts classes
Artistic and Creative Pursuits
- Graffiti murals with legal permits
- Music lessons or forming bands
- Theater and acting workshops
Sports and Physical Activities
- Joining local sports leagues (basketball, soccer)
- Martial arts classes for discipline and fitness
- Outdoor adventure clubs like hiking or camping
Educational Courses
- GED preparation classes
- Computer programming bootcamps
- Financial literacy workshops
How To Keep A Barely Legal Delinquent Teen Busy With Engaging Activities
It’s not enough to just offer options; the key is consistency and motivation. Here are some practical tips:
- Set Clear Expectations: Explain why staying busy is important, and what the consequences of negative behavior are.
- Involve the Teen in Decision-Making: Teens are more likely to engage if they choose activities themselves.
- Create a Routine: Having a daily or weekly schedule helps build structure.
- Provide Positive Reinforcement: Praise efforts and progress, no matter how small.
- Use Legal Counsel When Necessary: Sometimes legal professionals can recommend court-approved programs that combine supervision with engagement.
Comparison Table: Activities vs Benefits
| Activity Type | Skill Development | Social Interaction | Legal Benefits | Suitability for Delinquent Teens |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Community Service | Empathy, Responsibility | High | Often court-mandated | Very Suitable |
| Vocational Training | Technical Skills | Moderate | Helps with employment | Highly Suitable |
| Artistic Pursuits | Creativity, Expression | Moderate to High | Builds self-esteem | Suitable |
| Sports Activities | Physical Fitness | High | Teaches discipline | Suitable |
| Educational Courses | Academic Knowledge | Low to Moderate | GED can reduce legal risks | Very Suitable |
Practical Examples of Successful Engagement
In New York, several programs have shown promising results. For instance, the “YouthBuild” program combines construction training with education and community service, targeting at-risk youths including barely legal delinquent teens. Another example is the “Legal Outreach” initiative that offers mentorship and legal education combined with creative projects like spoken word poetry, which helps teens express themselves constructively.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls
Some efforts to keep delinquent teens busy fail because:
- Projects are too rigid or boring
- Lack of adult mentorship or supervision
- Ignoring the teen’s interests and strengths
- Not addressing underlying
Can Structured Routines Help Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Stay Focused and Busy?
Can Structured Routines Help Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Stay Focused and Busy?
Dealing with barely legal delinquent teens is never an easy task for parents, guardians, or legal professionals in New York. These young adults, hovering on the edge of adulthood, may struggle with focus, discipline, and staying out of trouble. One question that often arise is whether structured routines really can help keep these teens busy and more focused on positive activities rather than destructive ones. The answer is not simple, but evidence from behavioral studies and real-life examples suggest that structured routines might play a crucial role in redirecting the energy of barely legal delinquent teens toward more productive paths.
Why Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Struggle With Focus
Barely legal delinquent teens often face a mix of emotional, social, and psychological challenges. Many might have experienced instability in their lives, such as family issues, exposure to crime, or lack of positive role models. Their brains, still developing until mid-20s, have trouble regulating impulses and making long-term plans. Without proper guidance, these teens could easily fall into patterns of risky behavior or delinquency.
One reason why focus is hard for them is because they lack consistent structure in their daily lives. The absence of predictable routines means they often fill their time with unproductive or harmful behaviors. When there is no clear schedule, their time management skills remain underdeveloped, which makes it even harder to stay engaged in positive activities or responsibilities.
How Structured Routines Help
Structured routines provide predictable patterns that can create a sense of security and stability. When teens know what to expect in their day, they might feel more in control and less anxious about the unknown. This stability can reduce impulsive decisions and increase their ability to concentrate on tasks.
Some key benefits of structured routines include:
- Improved time management skills
- Reduced stress and anxiety
- Increased sense of responsibility
- Opportunities for skill-building and personal growth
- Better sleep patterns and physical health
In legal contexts, structured routines are often part of rehabilitation programs for delinquent youth. Courts and social workers frequently recommend schedules that combine education, counseling, and community service.
Practical Ways To Keep Barely Legal Delinquent Teens Busy With Engaging Activities
Engagement is critical. Simply creating a schedule without meaningful activities won’t work. Here are some practical ideas for activities that can keep barely legal delinquent teens busy:
Vocational Training
Offering hands-on skills like carpentry, automotive repair, or culinary arts can help teens develop marketable abilities while staying engaged.Community Service
Participating in community clean-ups, volunteering at shelters, or working with youth programs can foster a sense of purpose and connection.Physical Activities
Sports, hiking, or martial arts can channel energy positively and improve mental health.Creative Outlets
Art, music, or writing workshops provide emotional expression and reduce feelings of frustration or isolation.Educational Programs
GED classes, tutoring, or life skills workshops help build confidence and prepare for future independence.Counseling and Mentorship
Regular sessions with counselors or mentors give teens support and guidance through challenges.
A Comparison of Structured vs. Unstructured Days for Barely Legal Delinquent Teens
| Aspect | Structured Routine | Unstructured Day |
|---|---|---|
| Time Use | Planned activities, goal-oriented | Idle time, risky behaviors |
| Emotional State | Sense of control, less anxiety | Uncertainty, stress, boredom |
| Social Interaction | Positive peer and adult engagement | Negative peer influence, isolation |
| Skill Development | Consistent learning opportunities | Few or no skill-building activities |
| Legal Outcomes | Lower recidivism rates | Higher risk of re-offending |
| Physical Health | Regular exercise and sleep patterns | Irregular habits, poor health choices |
Historical Context of Using Structured Routines in Juvenile Rehabilitation
The concept of using structured routines for youth in trouble with the law dates back many decades. Early juvenile justice systems recognized that purely punitive measures were ineffective. Instead, programs were developed to teach discipline through daily schedules including school, work, and recreation. Over time, research has confirmed these approaches help reduce delinquent behavior.
In New York, many juvenile justice programs emphasize structure combined with therapeutic support. These models show better results than those relying solely on incarceration or punishment. Today, courts often mandate participation in such programs as part of probation or parole conditions.
Legal Implications and Support Systems in New York
For legal professionals working with barely legal delinquent teens, understanding the role of structured routines is vital. Judges, lawyers, and social workers can advocate for or design plans that incorporate daily structure to promote rehabilitation. Programs funded by the state or private
Conclusion
Keeping a barely legal delinquent teen engaged requires a combination of structure, positive reinforcement, and meaningful activities that channel their energy productively. Throughout this article, we explored various strategies such as encouraging involvement in sports, creative arts, volunteer work, and part-time jobs that not only occupy their time but also build valuable skills and self-esteem. Establishing clear boundaries and consistent communication is essential to help them understand expectations while fostering a supportive environment. By offering opportunities for personal growth and responsibility, parents and guardians can guide teens away from negative influences and towards a more promising future. Ultimately, staying patient and proactive plays a crucial role in transforming challenging behavior into constructive habits. If you’re facing similar challenges, start implementing these approaches today to help your teen develop into a responsible and motivated young adult. Your commitment can make all the difference in shaping their path ahead.